Swaged wire rope is a specially processed steel wire rope in which the outer diameter is mechanically compressed (swaged) after fabrication. This cold-forming process reshapes the rope into a more compact and uniform cross-section, enhancing its structural properties, surface smoothness, and load-bearing performance.
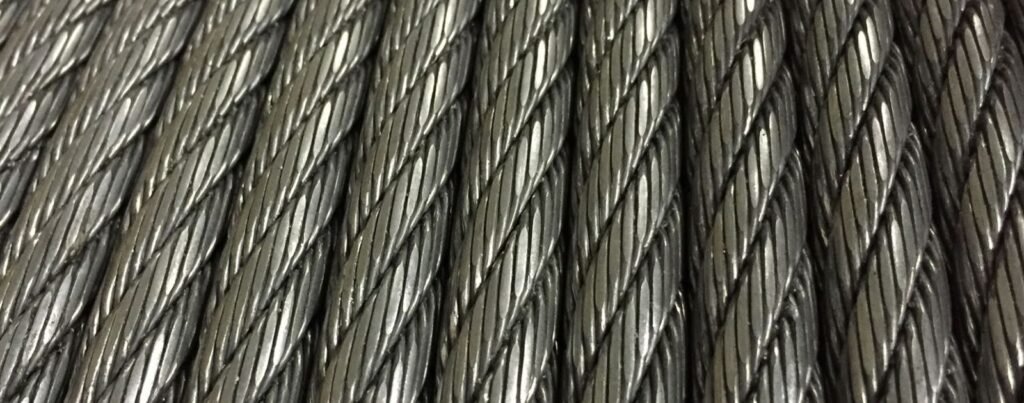

Wire rope is a versatile and essential component in many industries, widely used for lifting, rigging, mooring, and securing loads. It consists of multiple strands of metal wire twisted together to form a strong, flexible, and durable rope. Wire ropes are preferred over chains and synthetic ropes in many heavy-duty applications due to their superior strength, abrasion resistance, and fatigue life.
Swaged wire rope refers to wire rope that has undergone a specialized swaging process to attach fittings or terminations. Swaging is a cold-forming method that permanently deforms the rope or fitting under high pressure to create a secure mechanical connection. This process enhances the performance and safety of the wire rope assembly, making swaged wire ropes ideal for demanding environments and critical applications.
Swaged wire rope assemblies consist of a wire rope with fittings or end terminations that have been swaged (compressed or crimped) onto the rope. The swaging process involves pressing a fitting, such as a socket, sleeve, or ferrule, onto the rope using a hydraulic or mechanical press. This deformation tightly binds the fitting and rope, forming a seamless and highly durable connection.
Swaged wire ropes can be made from galvanized steel, stainless steel, or specialty alloys, depending on the application requirements. The swaged fittings themselves are usually made from steel or corrosion-resistant materials and may be coated or plated for additional protection.
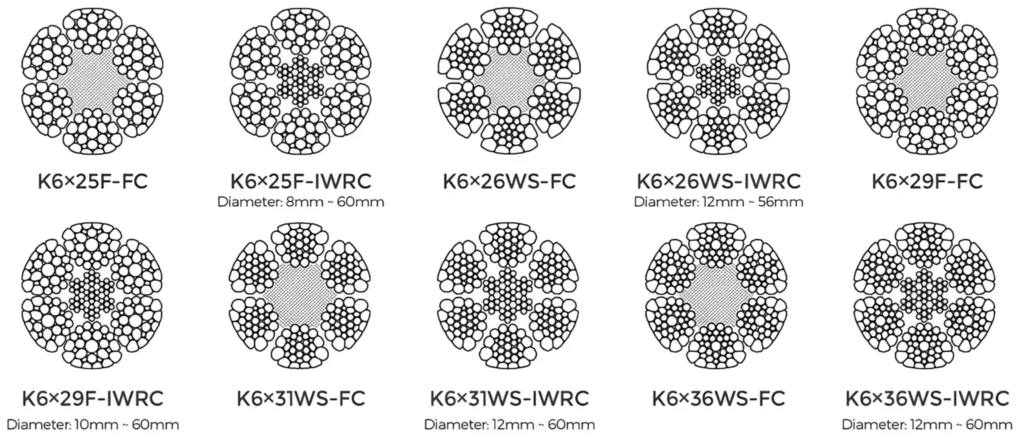
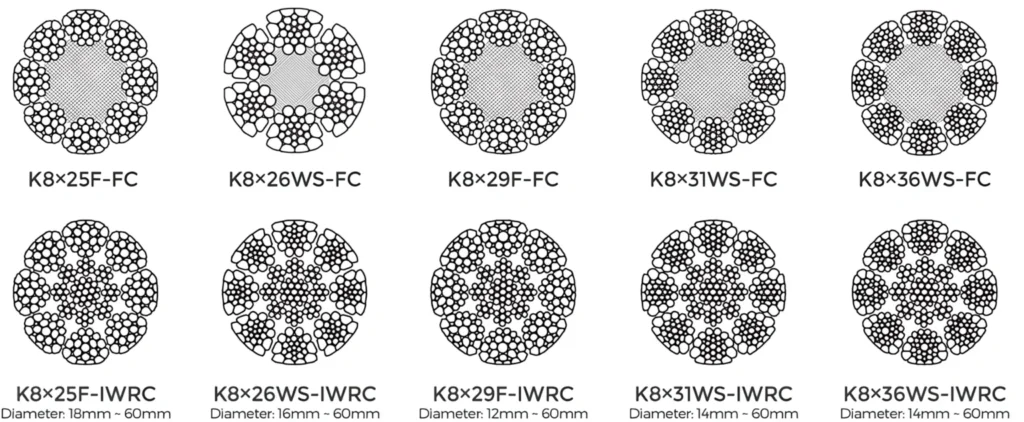
Before swaging, wire rope is manufactured by assembling individual wires into strands, and strands into the final rope configuration. The common wire rope constructions include:
6×19: Six strands, each with 19 wires, balanced for flexibility and strength.
6×36: Six strands with 36 wires, offering higher flexibility.
7×7, 7×19, 8×19: Different constructions providing varying flexibility and abrasion resistance.
The core of the rope can be fiber (natural or synthetic) or steel wire core (IWRC – Independent Wire Rope Core), which improves strength and durability.
The swaging process involves the following steps:
Preparation: The wire rope is cut to length, the end is cleaned, and any necessary pre-assembly tasks are completed.
Fitting Placement: The swage fitting (socket, sleeve, ferrule) is placed on the rope end.
Swaging: The assembly is inserted into a swaging machine. Hydraulic or mechanical presses apply high pressure to deform the fitting around the rope strands.
Inspection: The swaged connection is inspected visually and sometimes tested for strength and integrity.
Additional Treatments: Sometimes coatings, lubrication, or corrosion-resistant treatments are applied.
The entire process ensures a permanent, secure fitting that won’t slip or loosen during use.
There are various types of swaged fittings depending on the application and the desired connection type. Common fittings include:
Swage sockets are hollow fittings that are swaged onto the wire rope end, creating a strong mechanical connection. They are often used as end terminations or to connect to other components like shackles or turnbuckles.
Swage sleeves are cylindrical tubes placed over the rope and compressed to bind rope parts together or form loops. They are commonly used for making eyes or loops in wire ropes. Ferrules are smaller fittings used for similar purposes.
Studs and pins are used to create adjustable or removable connections. They are swaged onto rope ends and can be connected to other hardware.
Clips or couplings allow the joining of two wire rope ends or connecting wire rope to machinery or structural components.
Swaged wire rope assemblies offer multiple advantages compared to other termination or connection methods:
Swaging creates a mechanical bond that is often stronger than the wire rope itself. The high-pressure deformation ensures excellent load transfer and resistance to slippage.
Swaged fittings provide a smooth, compact termination without protruding parts, reducing snag hazards and simplifying handling.
The swaging process does not damage the wire rope strands, preserving rope flexibility and fatigue resistance. The durable fittings also resist corrosion and mechanical wear.
Swaged wire ropes can be customized to various sizes, constructions, and fitting types to suit a wide range of applications, including lifting, marine mooring, construction, mining, and aerospace.
Because the swaged fittings are permanent and tested, they reduce the risk of failure during operation, enhancing worker safety and equipment reliability.
Swaged wire rope assemblies are used extensively in industries where reliability, safety, and performance are critical.
Swaged wire ropes are frequently used in cranes, hoists, and lifting devices due to their ability to handle high loads and provide secure end connections.
In marine mooring, towing, and rigging, swaged wire ropes resist harsh environmental conditions, including saltwater corrosion and heavy wear.
Swaged wire ropes are essential in construction equipment, mining hoists, and cableways where strong, flexible ropes are required.
Specialty swaged wire ropes are used in control cables, structural supports, and safety devices in aircraft.
Wire ropes with swaged fittings are used in bridges, suspension systems, elevators, and architectural tensioning systems.
Swaged wire ropes and their fittings must comply with strict quality and safety standards. Important standards include:
ISO 9001: Quality management systems.
ISO 2408: Steel wire ropes — Minimum requirements.
EN 13411 series: Wire rope terminations.
ASME B30.9: Slings and rigging.
DIN 3050 / DIN 3091: Wire rope constructions and terminations.
API 9A: Wire ropes for drilling rigs.
Manufacturers perform tensile strength testing, fatigue testing, dimensional inspection, and nondestructive tests to ensure the swaged assembly meets specifications.
Many swaged wire ropes come with certification documents verifying compliance with standards, traceability, and test results, crucial for regulated industries.
Swaged wire ropes require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure long service life and safety.
Check for broken wires, corrosion, wear, and deformation around the swaged fittings.
Proper lubrication of the wire rope core reduces friction and corrosion but avoid lubricant ingress into swage fittings, which may cause slippage.
Periodically perform load tests to verify the strength and integrity of the assembly.
Replace wire ropes when:
Broken wire count exceeds standards.
Swaged fittings show signs of deformation or cracking.
Corrosion significantly weakens the rope or fittings.
The global market for swaged wire ropes is growing steadily due to increasing industrialization, infrastructure development, and safety regulations.
Advanced alloys and stainless steel grades improve corrosion resistance and strength.
Modern hydraulic and CNC swaging machines offer greater precision, ensuring consistent quality and performance.
Manufacturers increasingly offer tailor-made wire ropes with swaged fittings, complete with third-party certification for specialized industries like offshore oil, nuclear power, and aerospace.
When selecting swaged wire ropes, consider:
Load requirements: Maximum working load and safety factors.
Environmental conditions: Corrosion, temperature, abrasion.
Rope construction and core: Flexibility vs strength.
Fitting type: Compatibility with hardware.
Standards compliance: Industry-specific regulations.
Consulting with experienced suppliers ensures the correct specifications for your application.
Swaged wire ropes are a cornerstone in many heavy-duty industrial applications, providing unparalleled strength, safety, and reliability. Their specialized manufacturing process guarantees secure end terminations essential for critical lifting, rigging, and structural uses. With evolving technology and material innovations, swaged wire ropes continue to meet the demanding requirements of modern engineering and industrial sectors worldwide.
Kaiyuan road 36,Chunkou,Liuyang, Hunan,China.
info@steelwireropes.cn
info@wireropes.net
Phone : +86-15573139663
WhatsApp : ++86-15573139663
Get help choosing the right wire rope — fast, safe, certified.

WhatsApp us
Fill out a quick form to get a personalized quote tailored to your specific needs.
Note: Your email information will be kept strictly confidential.